Heat PumpRenewable Energy

What's a heat pump?
A heat pump is energy saving technology that conveys heat without the need to generate heat.
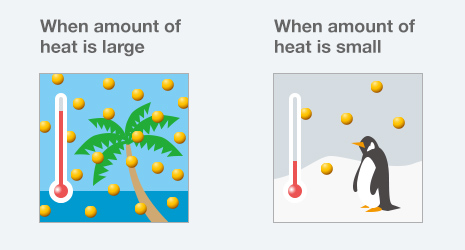
There is heat in the air even in places that are generally considered cold: for example, the North and South poles. However, because the amount of heat is small, these places feel cold.
When the amount of heat is large, the temperature is high. When the amount of heat is small, the temperature is low.
A heat pump is technology that controls temperature by transferring heat.
For example, because heating is performed by the transfer of heat from outdoors to inside the room only a little electricity is necessary. This provides energy savings.
How is heat transferred?
1Heat is carried by refrigerant.
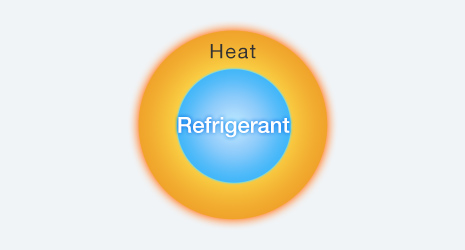
Refrigerant is a medium for conveying heat.
Air conditioners transfer heat while circulating refrigerant between the indoor and outdoor units.
Refrigerant is essential to an air conditioner and acts as its lifeblood.
2Heat Transfer
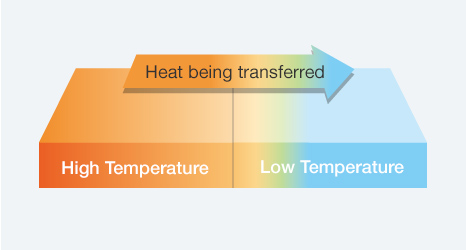
A physical law states heat is transferred from an area of high temperature to an area of low temperature.

For example, when a hot spoon is placed on top of a cold spoon, the cold spoon becomes warm.
Heat is transferred from the hot spoon to the cold spoon.
Heat transfer stops when both temperatures become the same.
3Utilizing the physical properties of heat, refrigerant carries heat and in the process the refrigerant condition changes to provide heating and cooling.
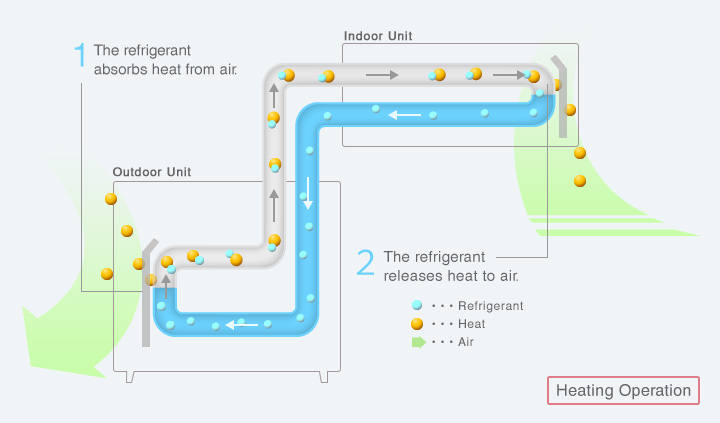
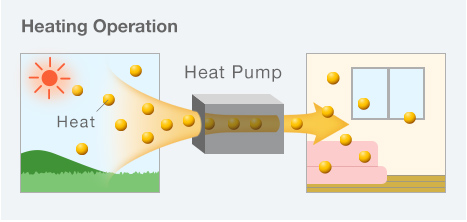
<Heating Operation>
Heat collected from outside is transferred inside the room.